DDR voltage adjustment is a crucial aspect in certain scenarios. It directly impacts the performance and stability of the DDR memory system. Understanding how to adjust it properly can lead to better overall system functionality, whether it's for enhancing performance or resolving potential issues.
Reasons for Adjusting DDR Voltage
In some cases, increased DDR voltage can lead to improved performance. When we overclock the system, for example, the default DDR voltage might not be sufficient. By increasing it within a reasonable range, we can enhance the data transfer speed of the memory, which in turn can make the overall system run faster. However, be aware that this also brings risks. If the voltage is set too high, it can cause overheating and potential damage to the memory modules. It's always a trade - off between performance and safety. Another reason could be to stabilize a flaky DDR system. Sometimes, with a particular hardware configuration, the DDR might not function stably at the default voltage. Adjusting it slightly can sometimes resolve this problem.

The Process of Adjusting DDR Voltage
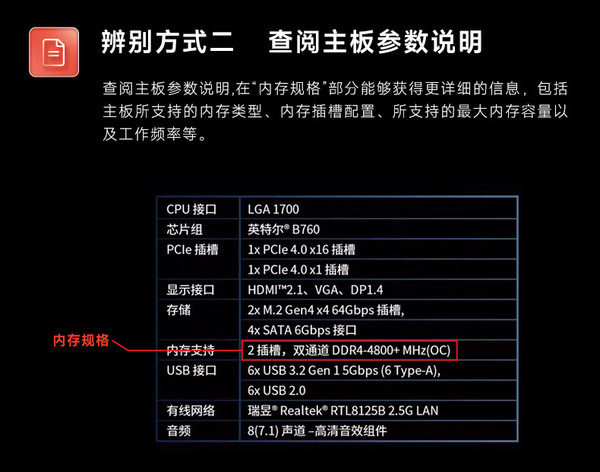
This typically involves accessing the BIOS or UEFI settings of the motherboard. Different motherboards have different interfaces, but generally, you need to find the section related to memory settings. Here, you can adjust the DDR voltage. It's crucial to follow the motherboard manufacturer's guidelines strictly. Some manufacturers provide a recommended voltage range for their DDR modules. Going beyond this range might void the warranty and cause hardware damage. When adjusting, it's advisable to make small incremental changes, like increasing or decreasing the voltage by 0.05 volts at a time, and then testing the system for stability.

Tools Needed
You don't really need any external tools in most cases. However, to monitor the changes effectively, some software utilities can be helpful. CPU - Z is a common tool that can show the current DDR voltage and other details about the memory. This allows you to check if the changes you have made in the BIOS or UEFI are actually taking effect. Another tool might be MemTest86. This is used to test the stability of the DDR system after the voltage adjustment. It runs various tests on the memory to ensure there are no errors.
Possible Risks
One of the major risks is hardware damage. DDR modules are sensitive to voltage changes. If the voltage is too high, it can lead to overheating, which can damage the components on the module. This not only renders the memory unusable, but it can also potentially affect other components in the system due to overheating. Another risk is instability. Even if the hardware doesn't get damaged immediately, an improper voltage adjustment can cause the system to crash frequently or cause data corruption. This can be very frustrating as it can lead to loss of work and data.
Tips for Safe Adjustment
Always start with the defaults. Before making any changes, note down the default voltage settings of your DDR modules. This gives you a reference point in case you need to revert back. Also, always research about your specific DDR module and motherboard combination. Some combinations have known - good voltage settings that can act as a guideline. And again, make small changes and test the system thoroughly each time. This way, you can catch any early signs of instability and avoid major problems.

When to Avoid Adjusting
If you are not experienced with hardware tinkering, it might be best to avoid adjusting the DDR voltage altogether. Novice users can easily make mistakes and cause more problems than they solve. If your system is running stable without any memory - related issues, there is no real need to adjust the voltage. Also, if your computer is under warranty and you are not sure if adjusting the voltage is allowed by the terms of the warranty, it's better to leave it as it is.
Here's a question for you readers: Have you ever had to adjust DDR voltage? If so, what was your experience like? I hope you find this article useful. Please like, share, and comment!